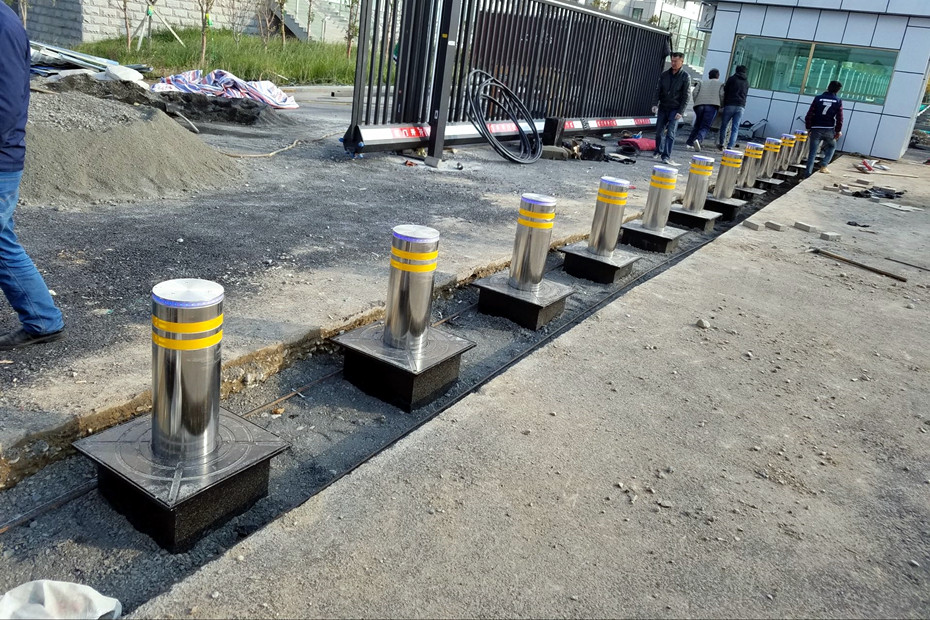
Effective access control is crucial at secured facilities. Both manual and automated bollard models can restrict vehicle entry, but offer different benefits based on site traffic needs. Examining key factors facilitates appropriate selection.
Manual Bollards Offer Constant Barriers
Manual bollards provide fixed physical impediments installed in permanent blocking positions. No mechanical adjustments are involved.
Fixed Bollards
Fixed bollards are permanently cemented or anchored into the ground by a heavy baseplate. Popular materials include:
- Concrete – Sturdy and damage-resistant, but prone to cracking from ground movement over time. Regular inspection is key.
- Steel – Available in various diameters and finishes. Galvanized or stainless steel offers lasting corrosion resistance. Steel bollards stand up to vehicle impact. Some decorative models feature unique shapes or patterns.
- Security-Rated – Engineered to achieve certified ratings (PAS 68, IWA 14, etc.) when impact-tested. Often specified at government facilities and other high-risk sites. Ratings indicate blast resistance levels.
Removable Bollards
Removable bollards are manually installed into mountings sunk in the pavement. No automation is involved. To open access, staff must lift each bollard out by hand using lifting hooks or specialty tools.
Usually used for temporary street closures or recurring restrictions that change on a predictable schedule. Removable models are often plastic or metal. The manual process is time-consuming and labor-intensive versus automated options.
Automated Bollards Allow Flexible Access
Automated bollards incorporate mechanical systems to raise and lower them with remote activation controls. This accommodates variable traffic levels.
Retractable Bollards
Retractable bollards lower fully beneath the pavement surface when access is needed. Either hydraulic pressure or electric motors power the retraction downward and raising back up.
Activation controls conveniently raise the bollards to block unauthorized vehicle entry when security is required. Retractable models suit sites like:
- Parking garages – Lower bollards to allow patron access, raise them after hours for perimeter security.
- Corporate campuses – Adjust access as needed while protecting buildings.
- Gated residential communities – Control vehicle entry but allow residents flexibility.
- Private roadways – Permit certain vehicle access but restrict general traffic.
Models are available in diameters suited for cars or larger trucks. Heavy-duty steel withstands vehicle impact when raised. Hydraulic versions provide exceptionally smooth operation.
Rising Bollards
Also termed pop-up bollards, these models stay concealed below ground in a housing until activated to rapidly rise up. No barrier is visible until the automated bollard extends upward.
Rising bollards create on-demand security with clean, unobstructed sightlines around public spaces, parks, or building entry areas. Remote controls quickly raise bollards when threats are detected. They can be lowered flush again afterward.
Keypad, Card Reader, or App Controlled
Many automated bollard systems integrate with keypads, card readers, or smartphone apps for convenient access control. Authorized users enter codes or swipe cards to raise and lower bollards.
This allows flexible access management without needing staff to manually move models. Audit trails document exact access times.
Automatic Safety Features
Advanced systems detect obstructions and reverse or halt bollard movement to prevent damage or entrapment. Battery backups keep them functional during power failures.
Considerations for Choosing Automated Bollards
- Traffic volume – More suitable for locations with more variable access needs versus sites requiring permanent restrictions.
- Frequency of access changes – If raising/lowering is needed multiple times daily, automated operation saves significant labor.
- Types of vehicles – Models must provide suitable height, diameter, and impact resistance for expected vehicles. Large truck access requires heavy-duty bollards.
- Power connections – Hardwired electric or solar options available to automate almost any location.
- Integration needs – Some systems can network with door access control panels, CCTV systems, guard booths, etc. for consolidated site management.
Aesthetic Bollard Options
Bollards are available in a range of finishes to complement different architectural styles and environments:
Decorative Models
Decorative bollards feature stylized shapes, patterns, materials, or detailing for enhanced visual appeal. They can incorporate:
- Ornamental shapes – Curved, fluted, or tapered steel or iron designs. Often topped with finials.
- Applied patterns – Tiles, emblems, mosaics, medallions, etc. can decorate bollard facades.
- Custom materials – Polished metals like brass or bronze. Natural stone types including granite, marble, and sandstone.
- Historic reproductions – Newer bollards crafted with traditional black iron, lantern, or acorn patterns provide a heritage aesthetic.
Decorative models are popular choices for public parks, pedestrian zones, historic sites, and streetscape revitalization projects. Durable cast iron is a common traditional material.
Custom Colors
Beyond basic black, white, or galvanized steel, bollards can be powder coated in custom colors to match surrounding architecture, landscaping, roadways, corporate branding, or other site elements. Vibrant reds, blues, and greens are bold options. Metallic coatings like bronze or silver tones integrate the look of metals without the higher cost.
Durable polyester or polyurethane powder coatings hold up better than paints against weathering, UV damage, and scratches. Proper surface preparation ensures long-lasting adhesion.
Camouflaged Bollards
Where prominent bollards would detract from a location’s aesthetics, models can incorporate outer coverings for disguise. Faux finishes that blend with surroundings include:
- Simulated tree bark – For placement in wooded areas or alongside landscaping.
- Brick, stone, or concrete cladding – To coordinate with building exteriors.
- Planters – With live vegetation planted at the base.
- Other environmental elements like drainage pipes, fire hydrants, or rubbish bins.
The disguises mask the security barriers from casual view while still providing protective stopping power when impacted.
Illuminated Bollards
Illuminated bollards integrate internal or external lighting elements for improved visibility and added ambiance. Common approaches include:
- LED light strips – Set into a clear polycarbonate tube or along translucent frosted sides. Provides soft glow.
- Spotlights or floodlights – Focused beam patterns aimed down to highlight bollard bases.
- Luminaires – Decorative fixture integrated into bollard top to emit light. More ornamental.
Illuminated bollards help mark pathways along dark roads or parks and provide directional wayfinding. Power options range from solar panels to hardwired electrical connections.
In Conclusion:
In summary, automated bollards enable flexible access control attuned to changing traffic levels throughout the day. Manual models provide fixed barriers where limitations can stay constant long-term. Evaluating site requirements determines which solution makes sense for the need at hand.